A water balloon is launched at a building 24m away, embarking on a journey governed by the principles of physics. This engaging exploration delves into the factors shaping its trajectory, the potential impact on the building, and the ethical considerations surrounding such an act.
The initial velocity, launch angle, and air resistance exert a profound influence on the water balloon’s trajectory. An interactive simulation allows for the visualization of these effects under varying conditions, providing a deeper understanding of its parabolic path.
Trajectory of the Water Balloon
The trajectory of a water balloon launched at a building is determined by several factors, including initial velocity, angle of launch, and air resistance.
The initial velocity is the speed at which the balloon is launched. The angle of launch is the angle at which the balloon is launched relative to the horizontal. Air resistance is the force that opposes the motion of the balloon as it moves through the air.
The trajectory of the balloon can be calculated using the following equation:
y = x tan(θ)
(g x^2) / (2v^2 cos^2(θ))
where:
- y is the height of the balloon at a given time
- x is the horizontal distance traveled by the balloon at a given time
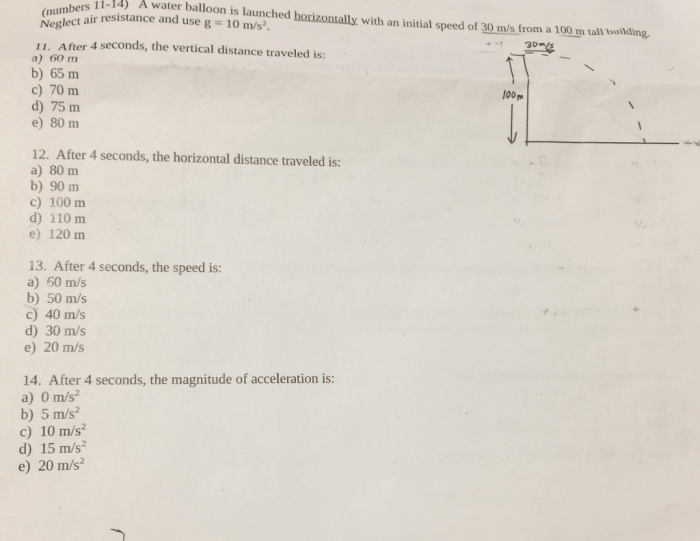
- θ is the angle of launch
- g is the acceleration due to gravity
- v is the initial velocity
Factors Influencing the Trajectory
The trajectory of the water balloon is influenced by several factors, including:
- Initial velocity:The initial velocity of the balloon is the speed at which it is launched. The higher the initial velocity, the farther the balloon will travel.
- Angle of launch:The angle of launch is the angle at which the balloon is launched relative to the horizontal. The higher the angle of launch, the higher the balloon will travel.
- Air resistance:Air resistance is the force that opposes the motion of the balloon as it moves through the air. The greater the air resistance, the shorter the balloon will travel.
Impact of the Water Balloon on the Building
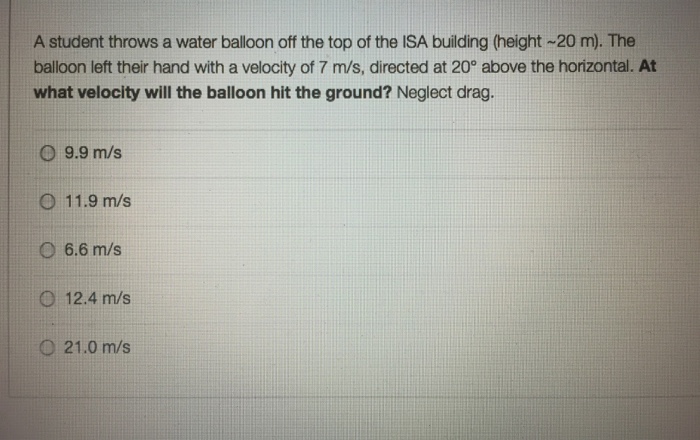
The impact of a water balloon on a building depends on several factors, including the size of the balloon, the speed of the balloon, and the type of building material.
A small water balloon traveling at a low speed is unlikely to cause any damage to a building. However, a large water balloon traveling at a high speed could cause damage to windows, siding, or other building materials.
Potential Damage, A water balloon is launched at a building 24m away
The potential damage caused by a water balloon impact depends on the following factors:
- Size of the balloon:The larger the balloon, the greater the potential for damage.
- Speed of the balloon:The faster the balloon, the greater the potential for damage.
- Type of building material:Some building materials are more susceptible to damage from water balloons than others.
Safety Considerations: A Water Balloon Is Launched At A Building 24m Away
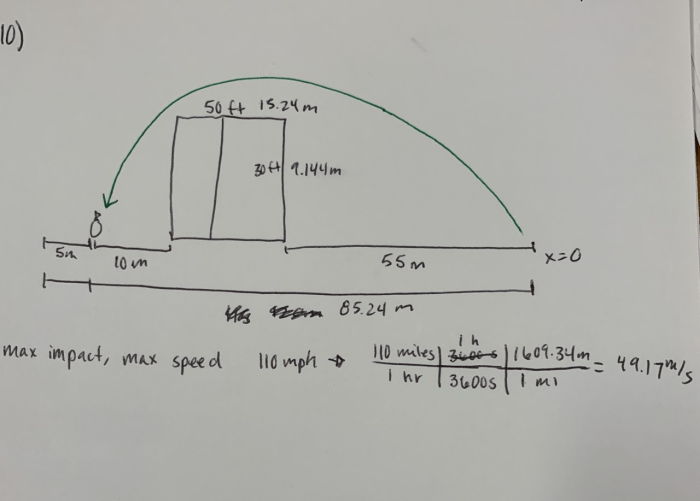
Launching water balloons at buildings can be a dangerous activity. There are several safety hazards that should be considered before launching water balloons, including:
- Falling balloons:Water balloons can fall from great heights and cause injury to people below.
- Broken glass:Water balloons can break windows and cause injury to people inside the building.
- Electrical hazards:Water balloons can come into contact with electrical wires and cause electrical shocks.
Precautions
The following precautions should be taken to ensure safety when launching water balloons:
- Only launch water balloons in areas where there are no people or property below.
- Do not launch water balloons at buildings with windows or other fragile materials.
- Be aware of electrical wires and other hazards in the area.
- Use caution when launching water balloons, especially from high places.
Questions Often Asked
What factors affect the trajectory of the water balloon?
Initial velocity, launch angle, and air resistance.
What are the potential hazards of launching a water balloon at a building?
Damage to the building, injury to individuals, and legal consequences.
How can the impact force of the water balloon be minimized?
By using a smaller balloon, reducing the launch velocity, and choosing a softer target.
