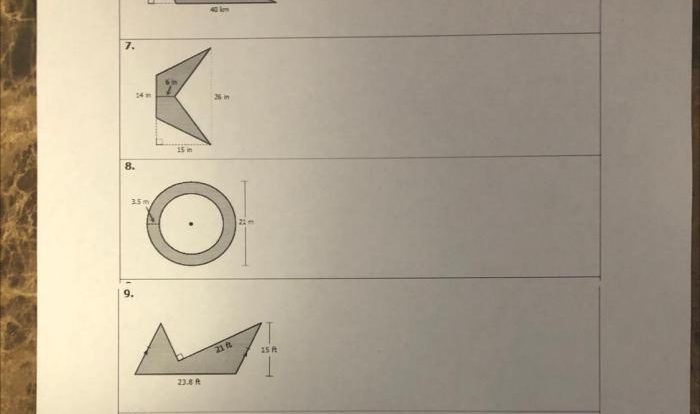
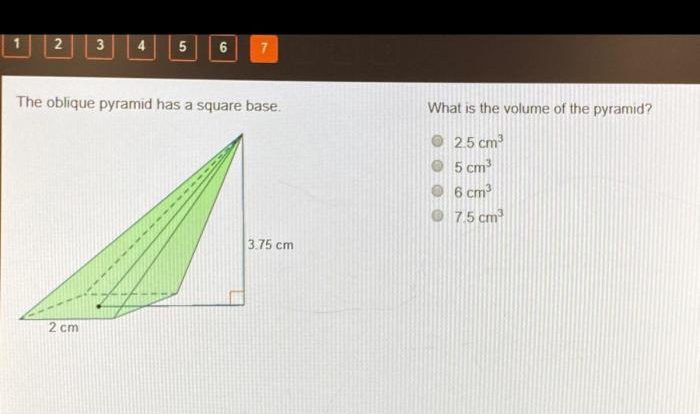
The realm of geometry unveils its captivating secrets as we delve into the intricacies of classifying 3D figures worksheet answers. This comprehensive guide empowers learners with the knowledge and skills to decipher the characteristics and properties that define these three-dimensional objects, embarking on a journey of discovery and understanding.
Through a systematic approach, we will explore the diverse shapes, properties, nets, cross-sections, and Euler’s formula, equipping readers with the tools to classify 3D figures with precision and confidence.
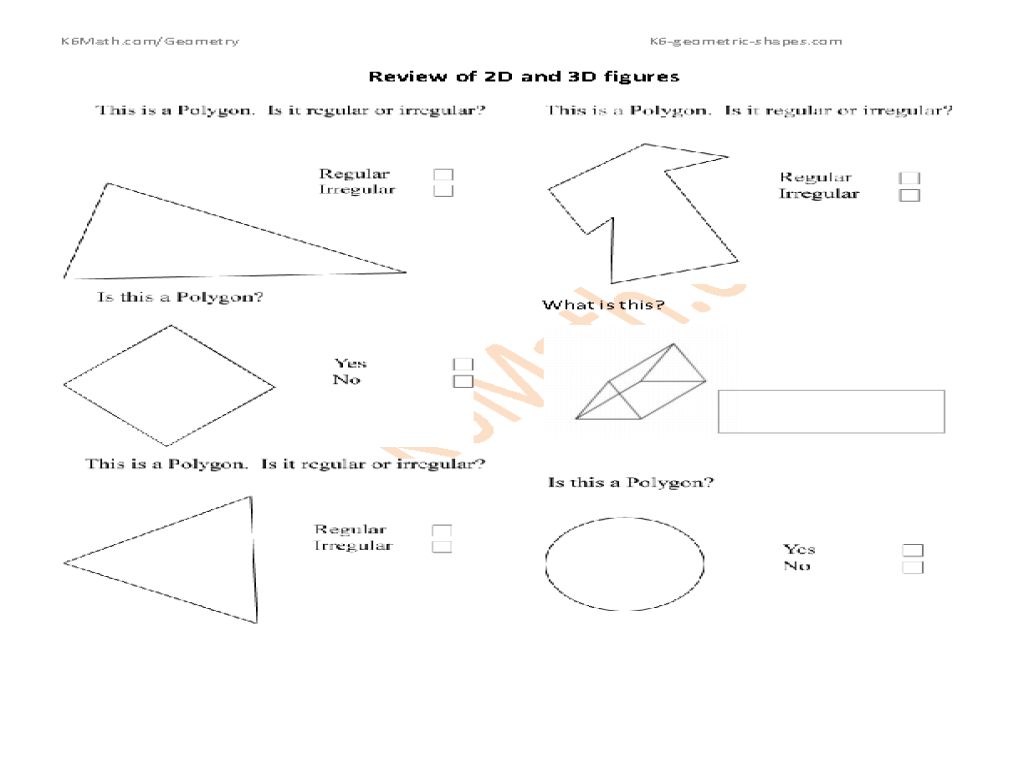
Classifying 3D Figures
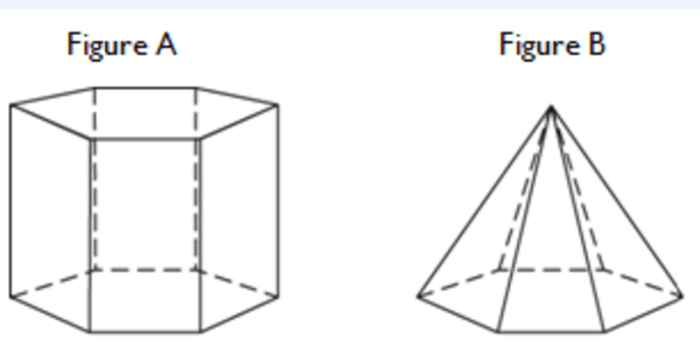
Classifying 3D figures involves determining their shape, properties, and other characteristics. This helps us understand their geometry and relationships with each other.
Classifying 3D Figures by Shape
| Shape | Number of Faces | Number of Edges | Number of Vertices |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cube | 6 | 12 | 8 |
| Prism | 2 (bases) + n (lateral faces) | 2n + 4 | 2n + 2 |
| Cylinder | 2 (circular bases) | 2 | 2 |
| Sphere | 1 | 0 | 0 |
To classify 3D figures by shape, identify the number of faces, edges, and vertices, and match them to the table.
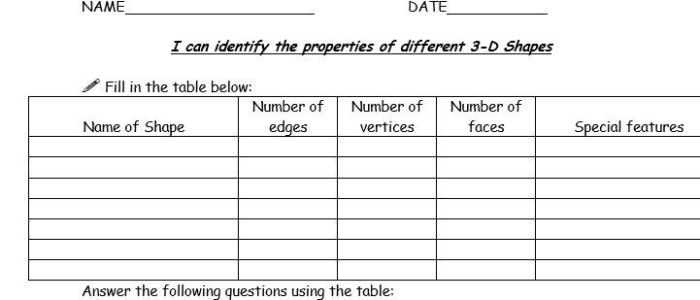
Classifying 3D Figures by Properties
3D figures can also be classified based on their properties, such as:
- Symmetry: Axis of symmetry, plane of symmetry
- Regularity: All faces and edges are congruent
- Convexity: No point lies outside the figure when connected to any two other points
By analyzing these properties, we can categorize figures as symmetric, regular, convex, or a combination of these.
Nets of 3D Figures
A net is a 2D representation of a 3D figure that can be folded to create the original shape.
- Cube: 6 squares
- Prism: 2 congruent bases + n rectangles
- Cylinder: 2 circles + 1 rectangle
Nets can be used to classify 3D figures based on their shape and the number of faces.
Cross-Sections of 3D Figures
Cross-sections are 2D slices of a 3D figure. Different types of cross-sections include:
- Perpendicular: Perpendicular to a base
- Parallel: Parallel to a base
- Oblique: Neither perpendicular nor parallel
Cross-sections can reveal the shape and properties of a 3D figure.
Euler’s Formula, Classifying 3d figures worksheet answers
Euler’s formula relates the number of faces (F), edges (E), and vertices (V) of a 3D figure:
F + V
E = 2
This formula can be used to classify 3D figures and check the validity of a given figure.
Top FAQs: Classifying 3d Figures Worksheet Answers
What are the different types of 3D figures?
There are various types of 3D figures, including prisms, pyramids, spheres, cones, cylinders, and cubes.
How can I classify a 3D figure based on its shape?
To classify a 3D figure based on its shape, you can examine its faces, edges, and vertices. For example, a cube has 6 square faces, 12 edges, and 8 vertices.
What is a net of a 3D figure?
A net is a two-dimensional representation of a 3D figure that can be folded to form the figure. Nets are useful for understanding the structure of 3D figures.
How can I use cross-sections to classify 3D figures?
Cross-sections are two-dimensional slices of a 3D figure. By examining the shape of the cross-section, you can gain insights into the figure’s overall shape.
What is Euler’s formula for 3D figures?
Euler’s formula for 3D figures states that V – E + F = 2, where V is the number of vertices, E is the number of edges, and F is the number of faces.